What are the Applications of a Proximity Sensor?
Proximity sensors have become indispensable in the modern automation industry. These sensors play a crucial role in identifying the presence, distance, or absence of an object without making physical contact. This contactless sensing capability is particularly beneficial for applications where touching could be hazardous, impractical, or simply not efficient. In this article, we explore various applications of proximity sensors, how they work, and their impact across industries. Whether you are a technician, engineer, or simply interested in automation technologies, understanding the diversity of applications for proximity sensors is key to comprehending their value.
Understanding Proximity Sensors and Their Types
Before diving into their applications, it is essential to understand what a proximity sensor is and the different types available in the market. A proximity sensor is a device that can detect the presence of a nearby object without any physical contact. This detection usually occurs through changes in electromagnetic fields or reflected signals.
There are several types of proximity sensors, each with its specific principle of operation and suitable application areas:
Inductive Proximity Sensors: Used primarily for detecting metallic objects. These sensors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. For example, they might be used to detect whether a metal machine part is in place during an industrial production cycle.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors: These sensors can detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including wood, plastic, and other materials. They work based on changes in capacitance.
- Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors: They use sound waves to determine the distance to an object and are highly versatile. These sensors are commonly used for detecting the presence and position of objects over longer ranges.
- Photoelectric Proximity Sensors: These sensors work by emitting light and detecting its reflection. They can be used for detecting clear and colored objects, and are especially useful in packaging industries.
Understanding these types is crucial when deciding the most appropriate sensor for your specific needs. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, which will influence its suitability for various applications.
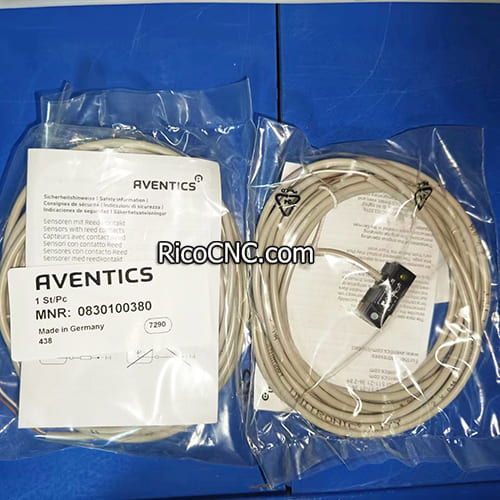

0830100380 Aventics Proximity Switch
Industrial Automation and Robotics
One of the most widespread applications of proximity sensors is in industrial automation and robotics. The automation industry thrives on accuracy, reliability, and safety, and proximity sensors contribute directly to these elements. In manufacturing environments, proximity sensors are used for:
Position Sensing: Proximity sensors help in determining whether an object, such as a component or tool, is in the correct position for the next step of the process.
- Object Counting: Inductive proximity sensors are often used to count metal parts as they move through an assembly line. Capacitive sensors are suitable for detecting non-metal items such as plastic parts.
- Safety Systems: Proximity sensors are commonly integrated into safety systems to shut down machinery when something or someone gets too close. Ultrasonic sensors, for example, are widely used for this purpose.
In robotic systems, proximity sensors are crucial in providing awareness of the robot's environment. Sensors help prevent collisions, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of robotic arms as they move parts across workspaces.
The reliability of these sensors is essential to automation. They reduce the risk of human error, enable precise repeatability of tasks, and ensure consistent production quality. To learn more about safety applications involving industrial automation, take a look at our Rexroth Pneumatic Solenoid Valve.
Automotive Applications

In the automotive industry, proximity sensors have several vital applications, which contribute significantly to safety and convenience. Here are some of the most common uses:
Parking Assistance: Ultrasonic proximity sensors are used in vehicles for parking assist systems, helping drivers detect nearby obstacles and park with ease. The sensors provide distance information, which is often represented with visual or auditory alerts.
- Collision Avoidance Systems: Many modern cars come equipped with proximity sensors as part of their advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These sensors help in detecting objects in blind spots, thereby avoiding collisions.
- Keyless Entry Systems: Capacitive proximity sensors are used in keyless entry systems. These sensors can detect the presence of the key fob and allow users to unlock and lock the car without physical contact.
These applications highlight how proximity sensors are making vehicles safer and more user-friendly. They are pivotal components of modern safety standards, offering both convenience and a reduction in accidents.
Manufacturing and Production Lines
In a manufacturing environment, ensuring that all processes work harmoniously is critical. Proximity sensors serve as the backbone of quality and reliability in production processes by detecting:
Presence and Absence: In production lines, inductive proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of metal parts to make sure that each stage of assembly proceeds as planned. For instance, in an automotive assembly line, sensors are used to verify that all necessary components are present.
- Material Level Sensing: Capacitive sensors can be used to monitor material levels in containers or hoppers. These sensors ensure that raw materials are always available, reducing downtime caused by running out of necessary components.
- Machine Tool Positioning: During machine operations, proximity sensors are used for determining the position of a machine tool or component. They help in providing feedback to control systems to adjust the position for accurate operation.
Proximity sensors help to ensure that all processes are streamlined, reducing waste, minimizing errors, and maximizing production output. Explore more about Wenglor Inductive Sensor used for detection and safety in production lines.
Medical Devices and Healthcare

In the medical and healthcare industry, proximity sensors are applied to enhance safety and improve the functionality of medical devices. Applications include:
Non-contact Monitoring: Capacitive proximity sensors are used in heart rate monitors, where they detect the minute movements of the body caused by the heartbeat.
- Automated Sanitation: Ultrasonic and capacitive sensors are used in automatic sanitizer dispensers, hand dryers, and other sanitation equipment to ensure minimal contact.
- Patient Monitoring Systems: Proximity sensors are incorporated into patient monitoring devices to detect body movement or lack thereof, helping to monitor conditions such as sleep apnea.
In the medical field, proximity sensors have helped develop non-invasive methods for monitoring, leading to increased patient comfort and more accurate data collection. To see an example of sensors used in healthcare applications, check out our SICK Contrast Sensors KTM Series.
Conclusion
Proximity sensors have emerged as a critical technology in the automation, automotive, medical, and consumer electronics industries. Their ability to detect without contact makes them invaluable for improving efficiency, safety, and the user experience in countless applications. From enhancing warehouse logistics to providing non-invasive monitoring in healthcare, the versatility of proximity sensors cannot be overstated.
To know more about proximity sensor types or find suitable components for your automation needs, feel free to contact us or explore our range of AVENTICS Magnetic Proximity Sensors. Our team is here to assist you in selecting the best solution for your application.
FAQs
1. How does an inductive proximity sensor work?
Inductive proximity sensors work by creating an electromagnetic field. When a metallic object enters this field, the sensor detects a change in inductance, signaling the object's presence.
2. What are the differences between capacitive and inductive proximity sensors?
Inductive sensors are designed to detect metallic objects, while capacitive sensors can detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, such as plastic, wood, or paper.
3. Can proximity sensors detect liquids?
Yes, capacitive proximity sensors can detect the presence of liquids by sensing changes in dielectric properties.
4. What type of proximity sensor is used in cars for parking assistance?
Ultrasonic proximity sensors are commonly used for parking assistance in cars because of their ability to measure distances accurately.
5. Are proximity sensors used in medical equipment?
Yes, proximity sensors are used in various medical devices for patient monitoring, non-contact operation of machines, and automated sanitation.
6. How do photoelectric proximity sensors differ from ultrasonic sensors?
Photoelectric sensors use light beams (typically infrared) for detection, while ultrasonic sensors use sound waves. This makes ultrasonic sensors better for longer-range detection, while photoelectric sensors are ideal for detecting transparent objects.